Abstract
Introduction: Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) involves the transplantation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSCs/HPCs) from autologous or histocompatible allogeneic donors. HCT restores bone marrow function after conditioning, high dose chemotherapy (Bendall, Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 2014). G-CSF, which prevents CIN, is also used to mobilize HSCs/HPCs (CD34+ cells) prior to HCT. Plinabulin (Plin), a small molecule with immune-enhancing anticancer activity, is under clinical development for cancer treatment and CIN prevention. Plin has anticancer activity in lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (pts) (Mohanlal, ASCO-SITC 2017), and patient-derived multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (Singh, Blood 2011). Single-dose-per-cycle Plin and pegfilgrastim (Peg) are equally effective for the prevention of Docetaxel (Doc)-induced grade 4 Neutropenia in NSCLC pts (Blayney; ASCO 2018; ASH 2016). Plin has a different MoA vs Peg; Plin acts through reversal of Doc-induced hematopoietic stem cell (LSK) maturation arrest in mouse bone marrow (Lloyd, AACR 2016) and increases neutrophil (N) demargination in pts (Blayney, SLB/IEIIS 2018). In contrast to Peg, Plin causes minimal bone pain, Plin ameliorates Doc-induced thrombocytopenia, and Plin does not increase N-to-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR) to immunosuppressive values of >5 in NSCLC pts (Blayney, IASCL 2018, ESMO 2018). Plerixafor (Pler), a chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) antagonist, inhibits CXCR4/SDF-1 binding facilitating CD34+ cell mobilization. Plinabulin does not inhibit CXCR4 (19% inhibition at 10μM Plin) in-vitro, thus Plin and Pler also have different MoAs. Although both G-CSF and Pler are effective in mobilizing CD34+ cells, up to 40% of pts fail to adequately mobilize HSCs/HPCs with G-CSF, or Pler combined with G-CSF (Jantunen, Eur J Hematol 2010). Predominantly due to high cost, Pler is not widely used. Since Plin has a different MoA vs G-CSF or Pler, Plin could be a valuable option for the mobilization of CD34+ cells prior to HCT, in particular if CD34+ response to G-CSF or G-CSF/Pler is inadequate. Peak CD34+ blood cell counts with G-CSF was ~6 cells/μL (Zarxio FDA Briefing Book, 2015). In a CIN phase 2 trial in NSCLC pts, designed to study Plin's efficacy to prevent Doc CIN, we also prospectively measured CD34+ peripheral blood cell count to assess whether Plin mobilized HSCs/HPCs.
Method: In study BPI-2358-105 (NCT03102606), NSCLC pts received 75 mg/m2 Doc with Plin at 5 mg/m2 (n=14), 10 mg/m2 (n=13) or 20 mg/m2 (n=14) on D1. Blood CD34+ cell counts were measured before (D0) and after (D 2,6,8 of Cycle 1 and D1 of Cycle2) Doc+Plin administration. CD34+ measurements were obtained in at least 9 pts on both D0 and D8 for each Plin dose. No blood draws for CD34+ cells were taken after D8.
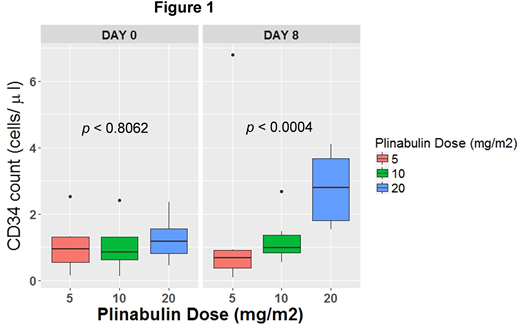
Results. Predose D0 CD34+ cell counts were comparable among Plin groups (p<0.8; figure 1, left). D8 was the earliest time point that showed increase in CD34+ cell counts. No blood draws for CD34+ after D8 in Cycle 1 was taken. Blood CD34+ cell count (Figure 1, right) on D8 had increased dose-dependently with Plin (p<0.0004; Jonckheere Terpstra test for dose-response). Change in CD34+ cell count from D0 was also increased dose-dependently on D8 (P<0.0004). In the 5 mg/m2 Plin group, median CD34+ cell counts on D8 had slightly declined, presumably due to myelosuppression with concomitant Doc. The frequency of pts with an increase in blood CD34+ cell count on D8 vs D0 was 89%, 60% and 50% in the 20, 10 and 5 mg/m2 Plin groups, respectively (P<0.0001 for dose response). Doc dose intensity was similar in all Plin dose arms.
Conclusion: Plin (20 mg/m2), an agent with anticancer activity for MM and NSCLC, mobilized CD34+ cells to clinically relevant blood counts in the vast majority of pts, through a MoA different from G-CSF or Pler. The CD34+ cell counts with Plin in the HCT setting is likely to be higher than observed in this CIN study, since concomitant myelosuppressive Doc was used with Plin. Furthermore CD34+ cell counts after D8 are likely to increase further with Plin, but this was not measured in this study. Based on current data evidence, Plin has the potential to become a viable option for the mobilization of CD34+ cells from the bone marrow prior to HCT, in particular in pts failing to respond to G-CSF or G-CSF/Pler.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal